The Rise of Resistance
In the realm of modern medicine antibiotics have been extensively recognized for their critical role in eradicating infections that historically resulted in significant mortality rates. However, the current era is marked by the burgeoning threat of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), which jeopardizes the efficacy of these vital therapeutic agents. The battle against AMR is complex, spanning from the agriculture fields to the very heart of our medical institutions. It’s a global challenge that calls for immediate action, collaboration, and innovation.
The sobering reality is that, according to statistics in 2019, drug-resistant microbial infections claimed more than 1.3 million lives and could claim more lives than cancer in the next few decades. The roots of this issue lie not only in healthcare settings but also in practices far removed from the operating table – such as the use of antimicrobials in agriculture.

Agriculture: The Frontline of Resistance
The misuse of antibiotics and antifungals in agriculture is concerning, highlighting the unintended consequences of such practices that, while aimed at protecting livestock, inadvertently foster environments conducive to the proliferation of resistant microbes. These resistant strains not only compromise animal health but also pose a significant risk to human populations, highlighting the urgent need for coherent regulations and policies that bridge the gap between human health and agricultural practices.
In this context, the adoption of water purification systems by farmers marks a pivotal advancement. By effectively disinfecting the drinking water of animals, these systems eliminate harmful bacteria not just from the water itself but also from the piping systems, thereby significantly reducing the animals’ exposure to potential pathogens. This innovative approach helps in mitigating the dependency on antibiotics for disease prevention, offering a sustainable solution that curtails the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Implementing infection prevention measures, such as the Aquatabs InLine system along with surface disinfection, plays a crucial role in maintaining animal health by ensuring they have access to clean, pathogen-free water and environments. Additionally, these practices are vital for safeguarding public health by addressing the challenges posed by antibiotic resistance.
Benefits of Aquatabs InLine:
Water is the largest nutrient consumed by any of our food producing animals. The following summarizes the results seen when using Aquatabs InLine for water purification and Septrivet 17 for surface disinfection by farmers:
Poultry Results
- Improved weight gain (9%) in chickens
- Dry litter
- Increased laying performance
- Fewer egg breakages
- Increased water in-take
- Reduced mortality
Pig and Cattle results
- Salmonella reduction
- Increased water in-take
- Increase in milk production
- Elimination of Listeria monocytogenes
- Broad spectrum surface disinfectant Septrivet 17 DAFM & DEFRA is approved to eliminate animals exposure to harmful pathogens within their housing environment

Antibiotic Resistance Escalation in Healthcare Facilities.
The 2022 report from the Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) underscores the troubling resistance levels among key bacterial pathogens. It records median resistance rates in 76 countries of 42% for E. coli resistant to third-generation cephalosporins and 35% for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Notably, in 2020, one in five urinary tract infections caused by E. coli showed lower responsiveness to standard treatments such as ampicillin, co-trimoxazole, and fluoroquinolones, complicating the treatment of routine infections.
Klebsiella pneumoniae, frequently found in the intestines, is presenting increased resistance against critical antibiotics. This uptick in resistance potentially necessitates more frequent use of last-resort antibiotics like carbapenems, with observed resistance to these drugs growing in various regions. With the efficacy of these last-resort medications waning, the danger of untreatable infections escalates. The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) projects a doubling in resistance to these critical drugs by 2035 compared to 2005, highlighting an urgent need for effective antimicrobial stewardship and broader surveillance efforts globally.
Fungal Resistance Concerns
The rise in drug-resistant fungal infections is under close observation by the World Health Organization (WHO) due to its significant public health implications. Treating fungal infections is notably challenging, often complicated by interactions with other drugs in patients co-infected with conditions like HIV. The rapid spread of Candida auris, a multi-drug resistant fungal infection, is particularly startling.
Tuberculosis (TB) plays a significant role in antimicrobial resistance, with multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) representing a critical challenge. MDR-TB, which resists the most potent first-line TB medications, requires more costly and toxic second-line treatments. In instances of extensive drug resistance, patients face severely limited treatment options, marking MDR-TB as a pressing public health and security issue. In 2022, only around 40% of individuals with drug-resistant TB received treatment.
Robust infection prevention policies and programmes within the healthcare sector can help to reduce the transmission of pathogens from patient to patient.
NaDCC’s Role in Reducing Antimicrobial Resistance
Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC) is a broad-spectrum disinfectant known for its efficacy against bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. Chemically, it is composed of a chlorine compound that releases hypochlorous acid (HOCl) when dissolved in water. The mechanism by which NaDCC acts involves the disruption of microbial cell walls and inhibition of enzymatic activity, leading to the death of the pathogen. This action is effective across a wide range of microorganisms, including those resistant to antibiotics.
NaDCC stands out in the fight against AMR due to its high efficacy in eliminating pathogens. It physically damages the cell structures of microorganisms, leaving little room for them to develop resistance mechanisms. Research and case studies have shown that regular use of NaDCC in healthcare settings significantly reduces the microbial load, including drug-resistant strains, thereby reducing the risk of infection transmission.
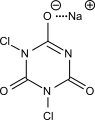
Comparatively, NaDCC is noted for its stability, ease of use, and effectiveness in a wide range of environmental conditions. This makes it a more reliable option than some traditional disinfectants, which may degrade more quickly or be less effective against certain types of resistant organisms. For effective implementation in healthcare environments, it’s crucial to follow recommended guidelines for NaDCC use. This includes proper dilution rates, contact times, and application methods to ensure optimal disinfection. Best practices involve routine cleaning of surfaces, medical equipment, and water systems with NaDCC
Seeking Solutions and Synergy
Recognizing the multifaceted nature of AMR, researchers and policymakers are advocating for a unified approach to tackle this issue. Solutions such as optimizing the use of antimicrobials across all sectors, restricting the use of critical antimicrobials in agriculture, and promoting infection prevention are crucial steps forward. Additionally, exploring alternatives to traditional antibiotics, like phage therapies, offers a glimpse of hope in this ongoing battle.
Global Cooperation: A Must
The COVID-19 pandemic emphasized the importance of global cooperation in addressing health crises. Similarly, combating AMR requires a concerted effort from international bodies, governments, and the scientific community. By sharing knowledge, aligning policies, and fostering international collaborations, we can hope to safeguard the future of antimicrobial treatments.
The Road Ahead
As we navigate through the challenges posed by AMR, it’s clear that no single sector can combat this issue alone. It requires a united front, innovative thinking, and sustained efforts. From improving dental care practices to supporting agricultural research, every action counts in the war against antimicrobial resistance. The stakes are high, but with collective action and determination, we can turn the tide against this global health threat.
https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240062702